Mercury is a planet in our solar system. It is the smallest of the eight planets. It is also the closest to the sun. Mercury goes around the sun the fastest of all the planets. Mercury has no moons.
Mercury's physical characteristics
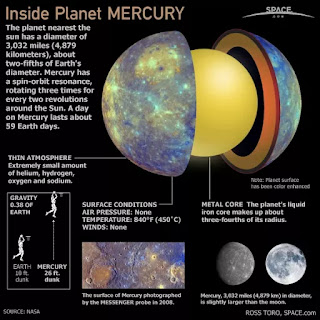
Because the planet is so close to the sun,Mercury surface temperature can reach a scorching 840 degrees Fahrenheit (450 degrees Celsius). However, since this world doesn't have a real atmosphere to entrap any heat, at night temperatures can plummet to minus 275 F (minus 170 C), a temperature swing of more than 1,100 degrees F (600 degree C), the greatest in the solar system.
Mercury's elliptical orbit takes the small planet as close as 29 million miles (47 million kilometers) and as far as 43 million miles (70 million kilometers) from the sun. If one could stand on the scorching surface of Mercury when it is at its closest point to the sun, the sun would appear almost three times as large as it does when viewed from Earth
Gravity
Gravity on Mercury
Gravity on Mercury is 38% of the gravity here on Earth. A man weighing 980 Newtons on Earth (about 220 pounds), would only weigh about 372 Newtons (83.6 pounds) landing on the planet’s surface. Mercury is only slightly bigger than our moon, so you might expect its gravity to be similar to the Moon’s at 16% of Earth’s. The big difference Mercury’s higher density – it’s the second densest planet in the Solar System. In fact, if Mercury were the same size as Earth, it would be even more dense than our own planet.
Gravity on Mercury is 38% of the gravity here on Earth. A man weighing 980 Newtons on Earth (about 220 pounds), would only weigh about 372 Newtons (83.6 pounds) landing on the planet’s surface. Mercury is only slightly bigger than our moon, so you might expect its gravity to be similar to the Moon’s at 16% of Earth’s. The big difference Mercury’s higher density – it’s the second densest planet in the Solar System. In fact, if Mercury were the same size as Earth, it would be even more dense than our own planet.



Comments
Post a Comment